While it can do many things, RSL is limited by the language. To enhance its functionality, one can implement a plugin using Pixar's RSLPlugin C++ API. For a sub-set of micropolygons my plugin writes RiCurves into an archive rib file that is referenced by a later beauty pass render. There are, therefore, two passes. The first creates moss-like geometry via my C++ plugin and must only be done once, the second generates the final image. For information on how to implement an archive rib, look here.

I tried to bake in the lighting into the rib file. Unfortunately this gave extraordinary values like color(126, 100, 50).
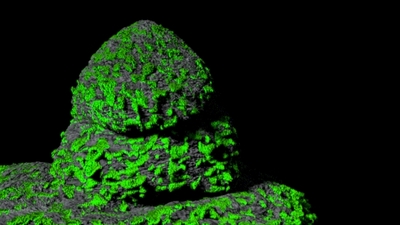
Applying a shader to the curves fixed the problem of trying to pre bake the colors into the moss. This way the plugin generated random variations of the user inputed color and then the shader on the geo container that is reading in the rib archive (how to do that here) takes care of the lighting.
| mossgen.sl |
| mossgenplug.cpp |
| perlin.h |









 RSS Feed
RSS Feed